1. 频率域图像增强
1.1. 傅里叶对数变换
f = imread('../pic/3/Fig0314(a)(100-dollars).tif');
F= fft2(f);
S = abs(F);
S = log10(1+S);
S1 = fftshift(S);
A = angle(F);
figure;
subplot(221);
imshow(f);
title('原始图像');
subplot(222);
imshow(S,[]);
title('傅立叶功率谱图像');
subplot(223);
imshow(S1,[]);
title('居中的傅立叶功率谱图像');
subplot(224);
imshow(A,[]);
title('傅立叶相位谱图像');

1.2. 低通滤波器
理想低通滤波器
巴特沃思低通滤波器
高斯低通滤波器
function [ U,V ] = dftuv( M, N )
%DFTUV 实现频域滤波器的网格函数
% Detailed explanation goes here
u = 0:(M - 1);
v = 0:(N - 1);
idx = find(u > M/2); %找大于M/2的数据
u(idx) = u(idx) - M; %将大于M/2的数据减去M
idy = find(v > N/2);
v(idy) = v(idy) - N;
[V, U] = meshgrid(v, u);
end
% 低通滤波器
function [ H, D ] = lpfilter( type,M,N,D0,n )
%LPFILTER creates the transfer function of a lowpass filter.
% Detailed explanation goes here
%use function dftuv to set up the meshgrid arrays needed for computing
%the required distances.
[U, V] = dftuv(M,N);
%compute the distances D(U,V)
D = sqrt(U.^2 + V.^2);
%begin filter computations
switch type
case 'ideal'
H = double(D <= D0);
case 'btw'
if nargin == 4
n = 1;
end
H = 1./(1+(D./D0).^(2*n));
case 'gaussian'
H = exp(-(D.^2)./(2*(D0^2)));
otherwise
error('Unkown filter type');
end
% 频率域滤波
function g = dftfilt(f, H,classout)
%DFTFILT Performs frequency domain filtering.
% G = DFTFILT(F, H) filters F in the frequency domain using the
% filter transfer function H. The output, G, is the filtered
% image, which has the same size as F. DFTFILT automatically pads
% F to be the same size as H. Function PADDEDSIZE can be used to
% determine an appropriate size for H.
%
% 'Original' The output is pf the same class as the input
% This is the default if CLASSOUT is not included
% in the call
%
% 'Fitpoint' The output is floating point of class single,unless
% both f and H are of class double,in which case the output
% also is of class double
%
%
% DFTFILT assumes that F is real and that H is a real, uncentered
% circularly-symmetric filter function.
% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.5 $ $Date: 2003/08/25 14:28:22 $
% Obtain the FFT of the padded input.
[f,revertclass] = tofloat(f);
F = fft2(f, size(H, 1), size(H, 2));
% Perform filtering.
g = ifft2(H.*F);
% Crop to original size.
g = g(1:size(f, 1), 1:size(f, 2));
if(nargin ==2 || strcmp(classout,'original'))
g = revertclass(g);
elseif strcmp(classout,'floatpoint')
return
else
error('undefined class for the output image');
end
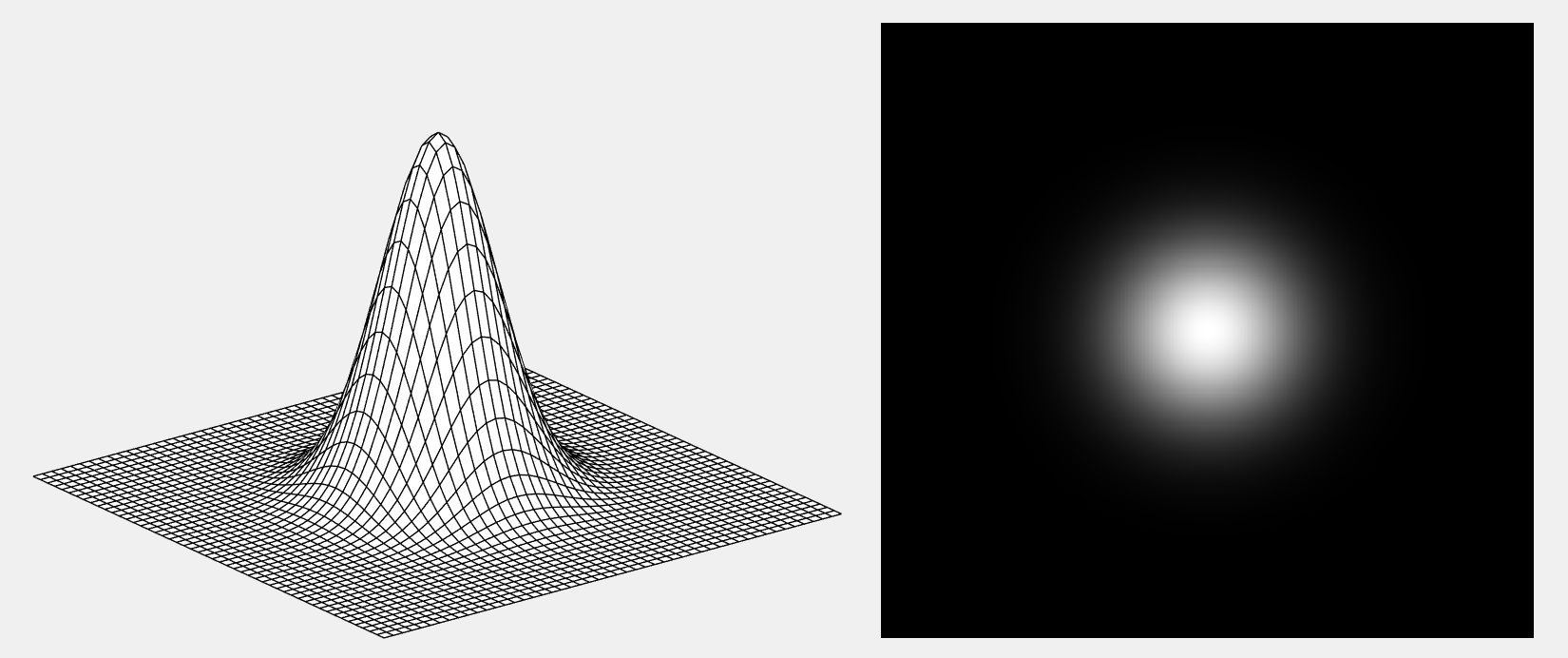
H = fftshift(lpfilter('gaussian',500,500,50));
figure;
mesh(H(1:10:500,1:10:500))
axis([0 50 0 50 0 1])
colormap([0 0 0])
axis off
grid off
figure;
imshow(H,[])
function [out, revertclass]= tofloat(in)
% [OUT,REVERTCLASS] = TOFLOAT(IN) converts the input image in to
% float-point.If IN is a double or single image,then OUT equals IN.
% Otherwise, OUT equals IM2SINGLE(IN). REVERSECLASS is a function handle
% that can be used to convert back to the class of IN
identity = @(x) x;
tosingle=@im2single;
table = {'uint8',tosingle,@im2uint8
'uint16',tosingle,@im2uint16
'int16',tosingle,@im2int16
'logical',tosingle,@logical
'double',identity,identity
'single',identity,identity
};
classIndex = find(strcmp(class(in),table(:,1)));
if isempty(classIndex)
error('Unsupported input image class.');
end
out = table{classIndex,2}(in);
revertclass = table{classIndex,3};
end
function g = gscale(f, varargin)
%GSCALE Scales the intensity of the input image.
% G = GSCALE(F, 'full8') scales the intensities of F to the full
% 8-bit intensity range [0, 255]. This is the default if there is
% only one input argument.
%
% G = GSCALE(F, 'full16') scales the intensities of F to the full
% 16-bit intensity range [0, 65535].
%
% G = GSCALE(F, 'minmax', LOW, HIGH) scales the intensities of F to
% the range [LOW, HIGH]. These values must be provided, and they
% must be in the range [0, 1], independently of the class of the
% input. GSCALE performs any necessary scaling. If the input is of
% class double, and its values are not in the range [0, 1], then
% GSCALE scales it to this range before processing.
%
% The class of the output is the same as the class of the input.
% Copyright 2002-2004 R. C. Gonzalez, R. E. Woods, & S. L. Eddins
% Digital Image Processing Using MATLAB, Prentice-Hall, 2004
% $Revision: 1.5 $ $Date: 2003/11/21 14:36:09 $
if length(varargin) == 0 % If only one argument it must be f.
method = 'full8';
else
method = varargin{1};
end
if strcmp(class(f), 'double') & (max(f(:)) > 1 | min(f(:)) < 0)
f = mat2gray(f);
end
% Perform the specified scaling.
switch method
case 'full8'
g = im2uint8(mat2gray(double(f)));
case 'full16'
g = im2uint16(mat2gray(double(f)));
case 'minmax'
low = varargin{2}; high = varargin{3};
if low > 1 | low < 0 | high > 1 | high < 0
error('Parameters low and high must be in the range [0, 1].')
end
if strcmp(class(f), 'double')
low_in = min(f(:));
high_in = max(f(:));
elseif strcmp(class(f), 'uint8')
low_in = double(min(f(:)))./255;
high_in = double(max(f(:)))./255;
elseif strcmp(class(f), 'uint16')
low_in = double(min(f(:)))./65535;
high_in = double(max(f(:)))./65535;
end
% imadjust automatically matches the class of the input.
g = imadjust(f, [low_in high_in], [low high]);
otherwise
error('Unknown method.')
end
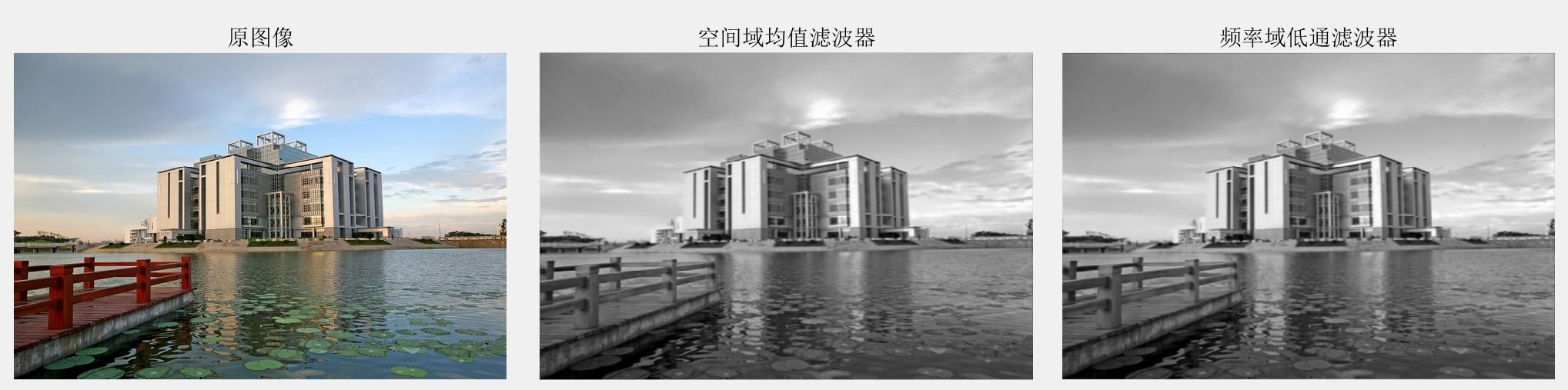
f = imread('../pic/1.jpg');
f2= rgb2gray(f);
h = [1,1,1;1,1,1;1,1,1];
f12 = imfilter(f2,h);
[r,c,c1]=size(f)
H = lpfilter('gaussian',r,c,100,1);
g = dftfilt(f,H);
subplot(131);imshow(f1);title('原图像');
subplot(132);imshow(f12);title('空间域均值滤波器');
subplot(133);imshow(g);title('频率域低通滤波器');

1.3. 高通滤波器
理想高通滤波器
巴特沃斯高通滤波器
高斯高通滤波器
function [ H, D ] = hpfilter( type,M,N,D0,n )
%HPFILTER creates the transfer function of a highpass filter.
% Detailed explanation goes here
%use function dftuv to set up the meshgrid arrays needed for computing
%the required distances.
[U, V] = dftuv(M,N);
%compute the distances D(U,V)
D = sqrt(U.^2 + V.^2);
%begin filter computations
switch type
case 'ideal'
H = double(D >= D0);
case 'btw'
if nargin == 4
n = 1;
end
H = 1./(1+(D0./D).^(2*n));
case 'gaussian'
H = exp(-(D0.^2)./(2*(D.^2)));
otherwise
error('Unkown filter type');
end
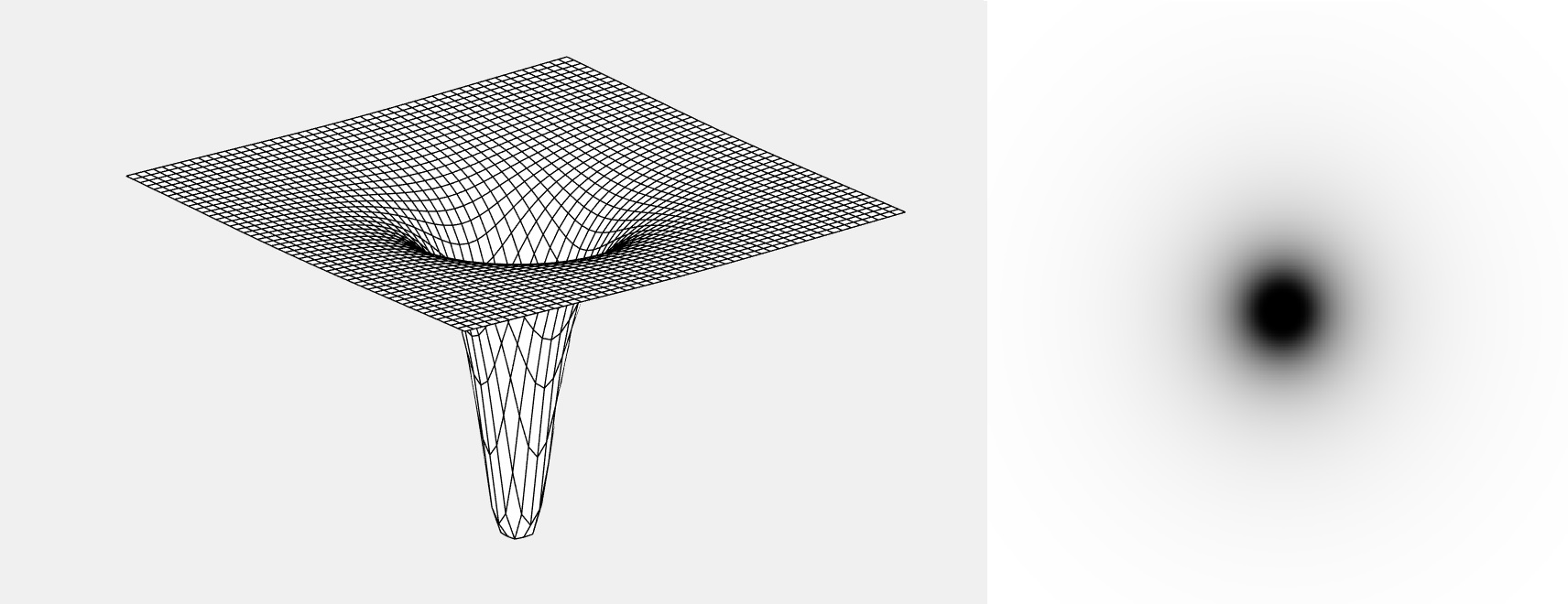
H = fftshift(hpfilter('gaussian',500,500,50));
figure;
mesh(H(1:10:500,1:10:500))
axis([0 50 0 50 0 1])
colormap([0 0 0])
axis off
grid off
figure;
imshow(H,[])
f = imread('../pic/1.jpg');
f2= rgb2gray(f);
h= [-1 0;0 1];
f12 = imfilter(f2,h);
[r,c,c1]=size(f)
H = hpfilter('gaussian',r,c,50,1);
g = dftfilt(f,H);
subplot(131);imshow(f1);title('原图像');
subplot(132);imshow(f12);title('空间域Robert滤波器');
subplot(133);imshow(g);title('频率域高通滤波器');

- 高频提升滤波
function PQ = paddedsize(AB,CD,PARAM)
%PADDEDSIZE Computes padded sizes useful for FFT-based filtering.
% Detailed explanation goes here
if nargin == 1 % int main(argc,**argv)
PQ = 2*AB;
elseif nargin ==2 && ~ischar(CD)
PQ = AB +CD -1;
PQ = 2*ceil(PQ/2);
elseif nargin == 2
m = max(AB);%maximum dimension
%Find power-of-2 at least twice m.
P = 2^nextpow2(2*m);
PQ = [P,P];
elseif (nargin == 3) && strcmpi(PARAM,'pwr2')
m = max([AB CD]);%maximum dimension
P = 2^nextpow(2*m);
PQ = [P,P];
else
error('Wrong number of inputs');
end
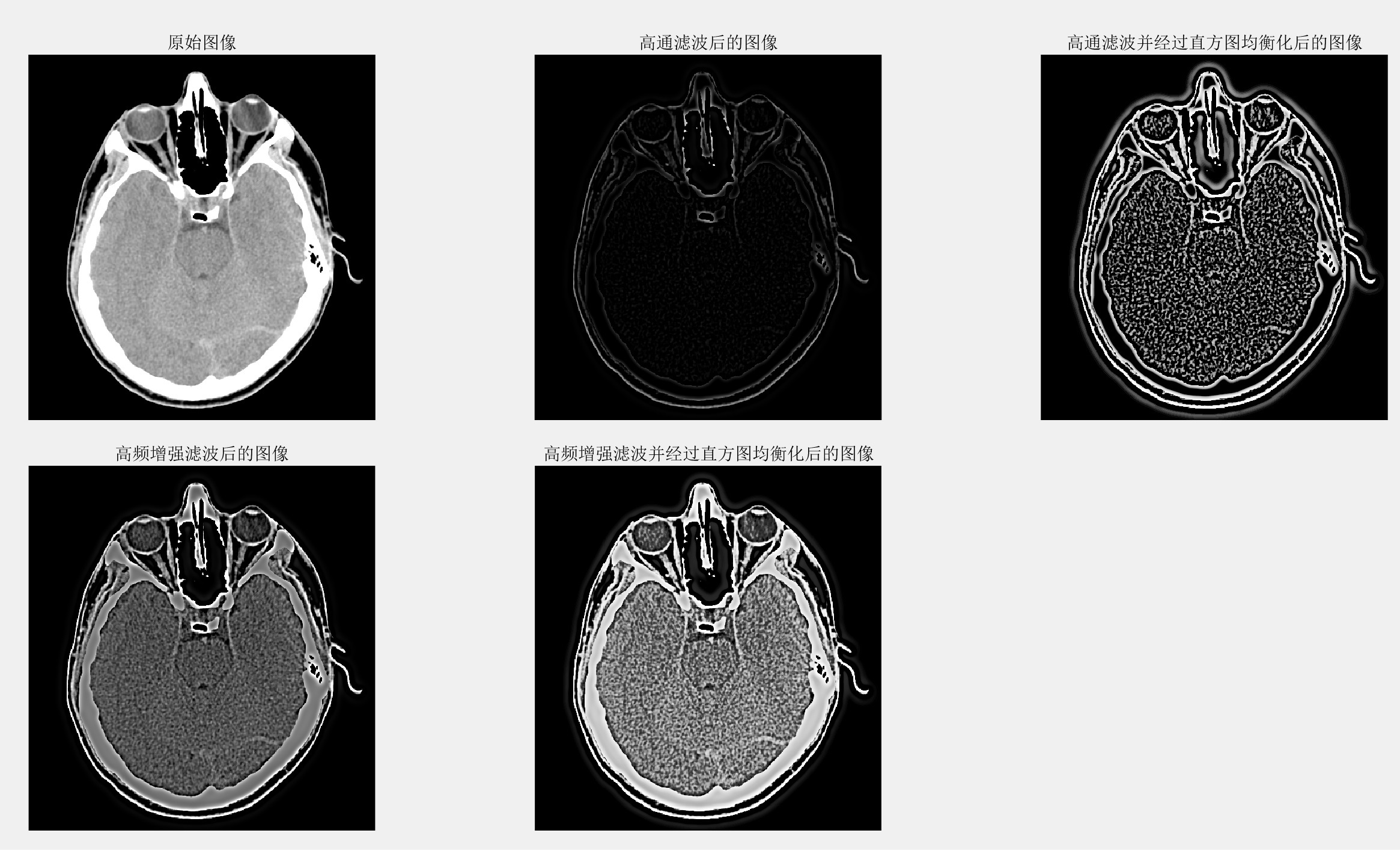
f = imread('../pic/3/Fig0359(a)(headCT_Vandy).tif');
PQ = paddedsize(size(f));
D0 = 0.05*PQ(1);
HBW = hpfilter('btw',PQ(1),PQ(2),D0,2);
H = 0.5+2*HBW;
gbw = dftfilt(f,HBW);
gbw = gscale(gbw);
gbe = histeq(gbw,256);
ghf = dftfilt(f,H);
ghf = gscale(ghf);
ghe = histeq(ghf,256);
figure;
subplot(231);
imshow(f);
title('原始图像');
subplot(232);
imshow(gbw,[])
title('高通滤波后的图像');
subplot(233);
imshow(gbe,[])
title('高通滤波并经过直方图均衡化后的图像')
subplot(234);
imshow(ghf,[]);
title('高频增强滤波后的图像');
subplot(235);
imshow(ghe,[]);
title('高频增强滤波并经过直方图均衡化后的图像');